3D printing breakthroughs are transforming industries by enabling the quick creation of affordable homes and biocompatible organs. You can now design structures with less waste and produce complex, customized products efficiently. This technology also supports sustainable practices by reducing material use and transportation emissions. As innovations in bioprinting and sustainable fabrication continue, industries evolve rapidly. Keep exploring to discover how these advancements are shaping the future of building, healthcare, and more.
Key Takeaways
- 3D printing now enables construction of fully functional printed homes, reducing costs and construction time.
- Advances in bioprinting allow for the creation of complex, functional organs for transplantation.
- Sustainable manufacturing benefits from 3D printing by minimizing waste and enabling eco-friendly materials.
- Rapid prototyping accelerates product development across industries, including architecture and healthcare.
- Future breakthroughs include personalized medicine, local on-demand production, and greener manufacturing practices.
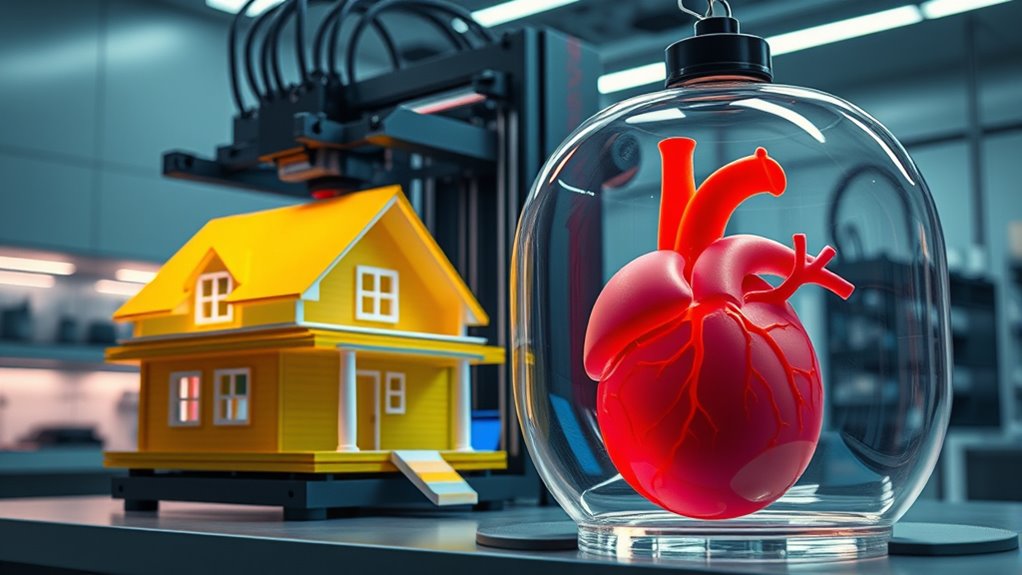
Recent advances in 3D printing are transforming industries and opening new possibilities for innovation. One of the most exciting developments is in bioprinting innovations, which are revolutionizing medicine and healthcare. Instead of relying solely on traditional manufacturing methods, you can now create complex biological structures, including tissues and organs, with remarkable precision. This technology allows you to layer living cells, scaffolding materials, and growth factors to produce functional biological parts. As a result, bioprinting is paving the way for personalized medicine, where you could someday have custom-made organs tailored to your unique biology. It also considerably reduces the need for organ donors, potentially saving countless lives.
In addition to its medical potential, 3D printing is becoming a champion of sustainable fabrication. Traditional manufacturing often involves wasteful processes, excessive material use, and environmentally harmful practices. However, with 3D printing, you can produce items directly from digital files, minimizing waste and optimizing material efficiency. This approach supports sustainable manufacturing because it allows you to create complex structures with less material and less excess scrap. Furthermore, you can use eco-friendly, biodegradable, or recycled materials for your projects, further reducing your environmental footprint. This shift toward sustainable fabrication is especially important as industries face increasing pressure to adopt greener practices and reduce carbon emissions. The ability to print on-demand also means you can cut down on transportation emissions, as products are produced locally rather than shipped from distant factories.
Additionally, 3D printing’s capacity for rapid prototyping accelerates innovation across sectors. You no longer have to wait weeks or months for mold-based manufacturing; instead, you can iterate designs quickly and cost-effectively. This speed empowers you to test new ideas and refine products with agility, encouraging experimentation that was previously too expensive or time-consuming. In architecture, for example, you can print scaled models or even entire building components, reducing waste and construction time. In the sphere of consumer products, customization becomes easier, giving you tailored items that meet specific needs or preferences. The advanced capabilities of 3D printing continue to expand, creating new opportunities for industries and creators alike.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Materials Are Most Commonly Used in 3D Bioprinting?
You mostly use biomaterials like hydrogels, collagen, and alginate in 3D bioprinting. These materials support cell growth and mimic natural tissues, enabling better tissue integration. Advances in biomaterial innovations improve printing resolution and stability, helping create more precise and functional organs. Your choice of materials depends on the desired tissue type and application, making these innovations essential for advancing bioprinting capabilities.
How Long Does It Take to Print a Full-Sized House?
Printing a full-sized house is like watching a time-lapse of a flower blooming; it can take anywhere from 24 hours to several days depending on the construction timeline and printing speed. Faster printers may produce a house in just a day or two, while more detailed designs or larger structures could take longer. Factors like design complexity, material type, and printer size all influence the total printing time.
Are 3D Printed Organs Fully Functional and Transplantable?
3D printed organs are still in development and not yet fully functional or transplantable. You should know that ethical considerations and regulatory challenges play a big role in their progress. Scientists are making strides, but guaranteeing safety and proper function takes time. As these hurdles are addressed, printed organs will become more viable for transplantation, but for now, they remain experimental and require further research and regulation to ensure patient safety.
What Are the Current Limitations of 3D Printing Technology?
Ever wonder why 3D printing still faces hurdles? You should know that scalability challenges limit mass production and complexity, making it tough to create large or intricate structures consistently. Regulatory hurdles also slow progress, as safety standards and approval processes lag behind technological advances. These limitations mean that while 3D printing is promising, it’s not yet fully ready for widespread, reliable use in critical fields like medicine or construction.
How Cost-Effective Is 3D Printing Compared to Traditional Manufacturing?
You’ll find that 3D printing can be more cost-effective than traditional manufacturing, especially with cost savings on materials and labor. It boosts manufacturing efficiency by reducing waste and streamlining production processes. However, initial setup costs and slower production speeds for large quantities can be limiting. Overall, for small runs or complex designs, 3D printing often offers significant advantages, making it a smart choice for innovative projects.
Conclusion
As you witness these 3D printing breakthroughs, it’s clear you’re stepping into the future—think of it as your own personal DeLorean speeding toward innovation. From printed homes to organs, you’re on the cusp of transforming lives and industries in ways once only imagined by sci-fi writers. Embrace this exciting era, because tomorrow’s reality is being built today, and you’re right there at the forefront of history. The future truly is a 3D masterpiece waiting to unfold.







